|
Allow user to extract data from ASCII string sent by equipment and present them as "tags" in the OPC Server. Designed for use with equipment that uses an operator command sequence. Its uses a pattern matcher to match the incoming data and extract the required information. Output is constructed with using C-style output formatting.
Channel Configuration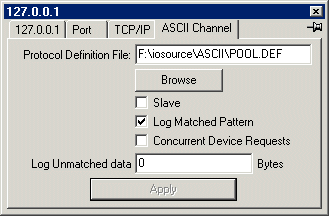
| Protocol Definition |
Path to file containing ASCII protocol definition. |
|---|
| Browse |
Browse for ASCII protocol definition file. |
|---|
| Slave |
Not implemented |
|---|
| Log Matched Pattern |
Log name of matched patterns to log file. |
|---|
| Concurrent Device Requests |
Requests are send to each device attached to this channel in parallel, without waiting for the response from the previous device. If disabled then only one request can be handled at a time per channel. |
|---|
| Log Unmatched data longer than |
Log all unmatched data longer than specified length. |
|---|
Protocol Definition Syntax
<Groups>:
<Group> ...
<Group>:
<GroupName>
<Action> ... |
<GroupName I>[fromI, toI]
<Action> ... |
<GroupName I>[fromI,toI]<GroupName J>[fromJ,toJ]
<Action> ... |
<GroupName I>[fromI,toI]<GroupName J>[fromJ,toJ]<GroupName K>[fromK,toK]
<Action> ...
<Action>:
Poll <Output Format> |
Read <Input Pattern>
<Data Type> <Item Name> <Replacement Format> ...
Output <Replacement Format> |
Write <Output Format>
<Data Type> <Item Name>
The Poll statement sends the output, it should be followed immediately by the Read statement which parse the expected response. The Poll statement is not required for unsolicited response. The Write statement is for issuing write request.
If no action is defined for a group, all matched input will be stripped from the input before other pattern matching, see StripVT100 in Vestas Wind Turbine example for stripping VT100 commands.
A line beginning with the '#' characters is treated as a comment line, the entire line is ignored. This comment line is used as the description for the next variable declared.
<GroupName>:
Name of Group
<GroupName>[First, Last]:
Name of Indexed Group
First is the first index, and Last is the last index e.g.
Turbine[1,9].Blade[1,16].Ring[1,4]
Read %u\i: Blade %u\j Ring %u\k Speed (%d) RPM
Word Speed $1
Will match inputs such as
1: Blade 1 Ring 2 Speed 456 RPM
2: Blade 2 Ring 3 Speed 654 RPM
and allow tags such as
Device1.Turbine1.Blade1.Ring2.Speed
Device2.Turbine3.Blade2.Ring3.Speed
<Data Type>:
Digital | Byte | Word | Long | Real | Double | String | Date
User requested data type
<Item Name>:
Name |
Name[Length] Subnames |
Name[FirstIndex, LastIndex] |
Name[FirstIndex, LastIndex, ReadSize, WriteSize]
Name of Item
| Length |
The number of elements in this item. The FirstIndex is set to 0. |
|---|
| Subnames |
A optional quoted string to define the sub name of elements in the array.
e.g. [6] "Motion=3,Metric=5" $1
will use bit 3 as the motion bit, and bit 5 as the metric bit |
|---|
| FirstIndex |
Defines the first index. |
|---|
| LastIndex |
Defines the last index. The number of elements is (LastIndex - FirstIndex) + 1 |
|---|
| ReadSize |
Defines the maximum number of elements that can be read in one request. |
|---|
| WriteSize |
Defines the maximum number of elements that can be written to in one request. |
|---|
When defining array, Name may be omitted.
<Input Pattern>:
<Metacharacters> [<Quantifier>] ...|
Each <Metacharacter> may be followed by a <Quantifier> to specify the minimum number of matches. A trailing '\' will cause the definition to continue to the next line.
<Metacharacters>:
| ^ |
Match beginning of line |
|---|
| . |
Match any character. .* or .+ is invalid |
|---|
| $ |
Match end of line. Must be the last character if used. |
|---|
| () |
Grouping. Up to 200 groups can be defined. |
|---|
| [] |
Character class. e.g. [a-z] for all lower case characters. |
|---|
| [^] |
Not in character class. e.g. [^a-z] for all non lower case characters. |
|---|
| \ |
Quote the next metacharacter |
|---|
| \t |
Tab |
|---|
| \n |
New line |
|---|
| \r |
Carriage Return |
|---|
| \x1B |
Hex char. eg \x1A for ctr-z |
|---|
| \w |
Match a "word" character (alphanumeric plus "_") |
|---|
| \W |
Match a non-word character |
|---|
| \s |
Match a whitespace character (space, tab, carriage return new line) |
|---|
| \S |
Match a non-whitespace character |
|---|
| \d |
Match a digit character |
|---|
| \D |
Match a non-digit character |
|---|
| \o |
Match an octal character (0-7) |
|---|
| \O |
Match an non-octal character. |
|---|
| \h |
Match a hexadecimal character (0-9,A-F) |
|---|
| \H |
Match a non-hexadecimal character |
|---|
| %04d |
Match four decimal digits, +, - or space |
|---|
| %04u |
Match four decimal digits |
|---|
| %04o |
Match four octal digits |
|---|
| %u |
Match all decimal digits |
|---|
| %f |
Same as [-+.0-9Ee]+ |
|---|
| %04x |
Match four hexadecimal digits |
|---|
| %c |
Match any character |
|---|
| %1b |
Match any 1 character |
|---|
| %2b |
Match any 2 characters |
|---|
| %2s |
Match any 2 characters |
|---|
| \a(0) |
Match the device address to the previous pattern |
|---|
| \c(...) |
See CRC/LRC/Checksum checking and generation |
|---|
| \i |
Set the I index to the previous pattern. |
|---|
| \j |
Set the J Index to the previous pattern. |
|---|
| \k |
Set the K index to the previous pattern. |
|---|
| \l(width,offset) |
Set the byte counter to the (previous pattern * width / 8) + offset |
|---|
| \L+ |
Match the number of bytes defined by \l |
|---|
| \p |
Set StartAddress to previous pattern |
|---|
| \e |
Set EndAddress to previous pattern |
|---|
| %4a |
Match four non space characters |
|---|
<Quantifiers>:
| * |
Match 0 or more times |
|---|
| + |
Match 1 or more times |
|---|
<Output Format>:
Use to C-style printf format to generate the output for transmission
%[flags][width][.precision][h]type
| flags |
| Flag | Meaning | Default |
|---|
| - |
Left align |
Right align |
|---|
| + |
Prefix output with + or - |
Prefix with - only for negative values |
|---|
| 0 |
Prefix Pad with '0' |
No padding |
|---|
| blank(' ') |
Prefix pad with blank |
No blank appears |
|---|
| # |
Prefix non zero value with 0, 0x or 0X (for o, x or X format) |
No blank appears |
|---|
|
|---|
| width |
Minimum number of characters in output. |
|---|
| precision |
Maximum number of characters in output. |
|---|
| h |
Treat input as a 16 bit value instead of a 32 bit value. |
|---|
| type |
| c |
Single byte character. |
|---|
| d |
Signed decimal integer. |
|---|
| i |
Signed decimal integer. |
|---|
| o |
Unsigned octal integer. |
|---|
| u |
Unsigned decimal integer. |
|---|
| x |
Unsigned hexadecimal integer using "abcdef". |
|---|
| X |
Unsigned hexadecimal integer using "ABCDEF". |
|---|
| e |
Real of the form [-]d.dddde[+-]ddd. Precision is the number of digits after the decimal point. |
|---|
| E |
Real of the form [-]d.ddddE[+-]ddd. Precision is the number of digits after the decimal point. |
|---|
| f |
Real of the form [-]dddd.dddd. Precision is the number of digits after the decimal point. Default value is 6. |
|---|
| g |
Use f or e format, whichever is more compact. |
|---|
| G |
Use f or E format, whichever is more compact. |
|---|
| s |
String. Precision is the maximum number of characters printed. |
|---|
| b |
Multiple byte character. Low byte first. |
|---|
| B |
Multiple byte character. High byte first. |
|---|
| z |
Multiple byte character. Low byte first. Swap Words |
|---|
| Z |
Multiple byte character. High byte first. Swap Words |
|---|
| a |
ASCII using 0123456789:;<=>?@ |
|---|
|
|---|
The % format may be followed by the following to use alternate output value. The default is to use the value supplied by the user (The OPC Client).
| \a(0) |
Device address |
|---|
| \c(...) |
See CRC/LRC/Checksum checking and generation |
|---|
| \i |
I index. |
|---|
| \j |
J Index. |
|---|
| \k |
K index. |
|---|
| \p(size,offset) |
(StartAddress / size) + offset. |
|---|
| \e(size,offset) |
((EndAddress + (size - 1))/ size) + offset |
|---|
| \l(size,offset) |
((BitCount + (size - 1)) / size) + offset. |
|---|
| \v(index) |
The index of group variable to be used. Use 1 for the first variable of the group. |
|---|
| \q(0) |
Sequence Number + 1 |
|---|
<Replacement Format>:
The Replacement Format is used to construct the string value of this item. The string value is converted from the decimal string to the decimal value <Data Type> specified and stored in the <GroupName>.<Item Name>. If the $n string is prefixed by (0x, 0o, 0b or h) then (hexadecimal, octal, binary or hexstring) conversion is used. The matched group are specified in the replacement format by $n, n starts from 1. $0 is a sequence number from 0 to 65535.
The string may be prefix by the following characters to control how the input is to be interpreted.
| b |
Copy bytes. |
|---|
| B |
Copy bytes. Swap each pair of bytes. |
|---|
| W |
Copy Words. Swap each pair of words. |
|---|
| R |
Copy Bytes. Reverse bit order. i.e. bit 0 becomes bit 7, bit 1 becomes bit 6 and etc., |
|---|
| v |
Expands 12 bits to 16 bits |
|---|
| h |
The input are ASCII characters (0-9,A-Z) |
|---|
Simple string operation can be performed if group n have the following prefixes
| $rn |
Reverse string |
|---|
| $x(value,start,length)n |
XOR each byte from start (decimal) to start + length (decimal) with value (hex). If length is zero, then perform operation on whole string. |
|---|
| $a(value,start,length)n |
AND each byte from start (decimal) to start + length (decimal) with value (hex). If length is zero, then perform operation on whole string. |
|---|
| $o(value,start,length)n |
OR each byte from start (decimal) to start + length (decimal) with value (hex). If length is zero, then perform operation on whole string. |
|---|
| $e(start,length)n |
Extract start (decimal) to start +length (decimal) from string. If length is negative then shorten string by -length. |
|---|
| $t(pos,from,to,length)n |
If the character at pos (decimal) at is equal to from (hex) then change it to (hex). If length is zero, then perform operation on whole string. |
|---|
| $+(length)n |
Lengthen string by length (decimal). |
|---|
Simple arithmetic operation on single value can be performed if group n have the following suffixes.
| +offset |
Add offset to value |
|---|
| -offset |
Subtract offset from value |
|---|
| *factor |
Multiple value by factor |
|---|
| %factor |
Divide value by factor |
|---|
| &factor |
Remainder of value after dividing by factor |
|---|
Timestamping Data
The Date data type will timestamp all subsequent tags with input date string. See csvtime.def for an example of timestamping data from a csv file. The minus character should not be used as separator.
Example of date usage in which the time of day is given in the number of half hour starting from 1. $2/$4 could be the year (year greater than 1000)
Date Time $2/$3/$4 0/$5-1*30/0
Device Initialization Sequences
Groups defined before and including the GroupNamed "Begin" are automatically used as the device initialization sequences when the device is first opened.
Message Header and trailer
All messages may have a predefined header and trailing sequence of characters, by defining the following at the beginning of the definition file.
| STXPOLL |
Header for Poll messages |
|---|
| STXREAD |
Header for Read and Peek messages |
|---|
| STXWRITE |
Header for Write messages |
|---|
| ETXPOLL |
Trailer for Poll messages |
|---|
| ETXREAD |
Trailer for Read and Peek messages |
|---|
| ETXWRITE |
Trailer for Write messages |
|---|
| STX |
Header for Poll, Read, Peek and Write messages if a specific one is not defined |
|---|
| ETX |
Trailer for Poll, Read, Peek and Write messages if a specific one is not defined |
|---|
| ConvertToASCII |
Convert input to space separated ASCII values |
|---|
See Modbus Master RTU for an example.
Device Configuration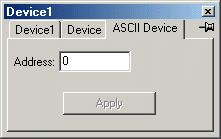
| Address |
Address of Device. Can be use to output device address or parse input device address. See \a metacharacter. |
|---|
Protocol Definition Files
Accuray 1180M
Avtron K936
Durant Ambassador Series Count Control Model 57601-400.
Modbus Master RTU
NEG Micon Wind Turbines
Symbol LS4071 Barcode Scanner
Red lion web server
VESTAS Wind Turbines
Weigh-Tronix Model WI-120 Indicator
Toshiba LCU/SFC OPC Server
Data from Multimeter QM1538 with RS232 inteface
ASCII Driver FAQ | 
